Securing IP-based Communication in Smart Object Networks
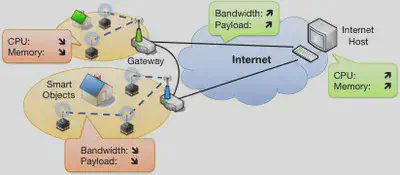
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) have long lived isolated lifes providing special-purpose functionality. This isolation allowed to deploy application-specific communication protocols as well as scenario-specific security solutions. However, it also led to networked islands that are hardly interconnectable. Recently, a variety of industries have realized the advantages of an easy to integrate sensor network architecture and push towards IP technology as the common denominator for communication in constrained networks. Example scenarios include industrial and home automation networks based on Smart Objects (i.e., IP-equipped sensors and actuators). The use of IP technology is envisioned to allow reuse of existing protocols as well as already deployed network infrastructure. Furthermore, IP enables direct communication between individual Smart Objects and Internet hosts in a conceptually elegant and simple way. However, while providing exciting new ways of interaction with the physical world, the security implications of these new network scenarios are challenging and not yet well understood.