Horizon - Parallel Network Simulator
Discrete event-based simulation is a commonly used evaluation methodology throughout the development process of networked systems. However, it currently faces at least two significant challenges: First, recent advances in wireless communication technology demand highly accurate simulation models, resulting in a steep increase in model complexity and runtime requirements. Second, multi-processor computers constitute the de-facto default hardware platform even for desktop systems, thus providing cheap yet powerful “private computing clusters”. As a result, the parallelization of discrete event simulations significantly gained importance and is therefore (again) in the focus of active research.
Model Complexity: Simulation models of wireless networks typically require a considerably more detailed modeling of the lower network layers than models of wired networks. In particular, the wireless channel and the physical layer demand precise models to capture the subtle effects and interactions of advanced wireless communication technologies such as MIMO transmissions or successive interference cancellation. Consequently, simulation run-times increase drastically which in turn hampers the development process and in-depth evaluations.
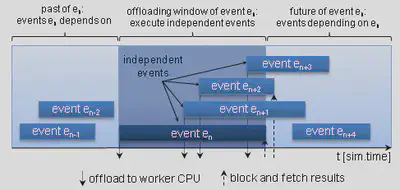
Parallel Discrete Event Simulation: Being an active field of research for more than two decades, parallel discrete event simulation is supported by a wide range of network simulation frameworks. Despite this tool support, creating a parallel simulation model is still challenging and running simulations on a distributed simulation cluster is complex. At the same time, the increasing number and speed of processing cores in today’s commodity hardware makes a higher degree of parallelization very attractive and cost-effective for speeding up network simulation. Nevertheless, a key challenge in parallel simulations, in particular of wireless networks, is the efficient utilization of the available processing power.
In this project we address these challenges by developing a novel parallelization architecture that specifically focuses on the efficient simulation of wireless network simulation models on state-of-the-art multi-core computers. We primarily investigate means of extracting a maximum degree of parallelism from a given simulation model and schemes to achieve a balanced work load across computing cores.
Current State
The foundations of Horizon have been laid in the last years, the basic system is already matured. Today’s research focuses on more sophisticated techniques. We increase the scalability of Horizon by combining it with distributed simulation and investigate techniques to increase the knowledge about event dependencies by learning automatically at both run-time and compile-time.